Our Vision of Risk Analysis
Risk Analysis: Why Complicate Things When They Can Be Simple?
A successful risk analysis links risks to objectives. This contributes directly to creating buy-in from stakeholders to simplify the analysis process. The risk analyses become more vital when they become part of the organizational rhythm.
Full Trial
Only 30 minutes
Without obligation

The Three Components of a Successful Risk Analysis.
Risk Inventory
Clarity of objectives and context creates a good organization-wide risk picture. This makes it easier to identify all risks. It also brings out stakeholders and actively involves them.
Analyze Risks
The risk inventory can now be structured by, for example, determining probability x impact and a strategy. This gives the broad risk profile focus and priority.
Monitor Risks
The risk profile leads to the right actions and measures. Monitoring shows whether the strategy is effective and where adjustments or improvements are necessary. This creates a vital risk profile and an involved organization.
Keep Risks Top-of-Mind with a Risk Analysis
A good risk analysis provides insight into the impact a risk can have on elements such as the value of the company, the image, the brand and the reliability. To achieve this, the impact of a risk (in relation to the business objectives) is often assessed at multiple levels. Think of divisions, functions, projects and operational units. It often happens that risks which are assessed as important in a department/project have no or minimal impact on the organizational objectives. By structuring risk analysis, risk maps are created on different levels. Linking risks to measures and actions provides the organization with a risk matrix that can be actively monitored. Monitoring and reporting keeps risks top-of-mind.

Three Lines Model
1st line
2nd line
3rd line
The Three Lines of Defense model from The Global Institute of Internal Auditors was updated in July 2020.
The functions are not only intended to protect the value of the organization, but also to increase it. As a result, we no longer talk about ‘lines of defense’ or ‘lines of defence’.
The goals of the organization are central to all functions. The functions are not silos, but coordinate and work together; each from his own role. The design of the model must be geared to the risks and specific situation of the organization.
The 3LM establishes a stronger link with the objectives of the organization.

1st line
This group is ultimately responsible for the choices made and the risks taken in daily practice .
You want to optimally support the people who are responsible for the most important activities and processes in an organization. GRC information is relevant, but often only if you have to. How do you make it easier for them? How is risk management going to live for them? Do they know within which frameworks they have to operate? And how do you effectively conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment without immediately bombarding all teams with a questionnaire of more than 100 questions?
Key words are: Accountability and reporting.
< p>
2nd line
This group develops the systems for a good process of risk management and control , always supporting the ‘business’.
The risk manager, controller, auditor, compliance or security officer (CISO) wants a clear register of risks, controls, compliance sets and, for example, related incidents. NARIS GRC helps the GRC Professional with insight, completeness. Whether you work on the basis of a Risk Control Framework or only do control testing, want to do internal and external audits, or want to comply with a standard. With our knowledge and the flexibility of NARIS GRC you can steer with guts.
Keywords are: Delegation, direction, resources, supervision

3rd line
This group provides assurance to top leadership (assurance) on the quality of direction and control in certain areas within the organization.
Supervisors, Boards of Directors/Supervision/Commissioners, external auditors or accountants, as an internal auditor you want to report in an effective and relevant way. NARIS GRC can help you with those reports; whether it concerns assurance of audits or controls, risks at chain partners or objectives of the organization itself. From detail to dashboard, internally or externally; look back to steer forward. Fueled by useful GRC information so that the right assurance can be given.
Keywords are: Alignment, communication, coordination, cooperation

Types of risk analyses
Qualitative analysis
Qualitative analyzes (such as interviews, workshops, surveys and benchmarking).
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analyzes (such as modelling, decision trees, Monte Carlo simulations).
Error tree analysis
Analysis and calculation of the probability of the most undesirable reaction (top event).
Link Risks to Objectives
The impact of risks on your organization’s value, brand, image and reliability can only be determined by linking risks to objectives. NARIS GRC shows at a glance what impact risks have on objectives. This creates an organization-wide support base and insight into the value of GRC.
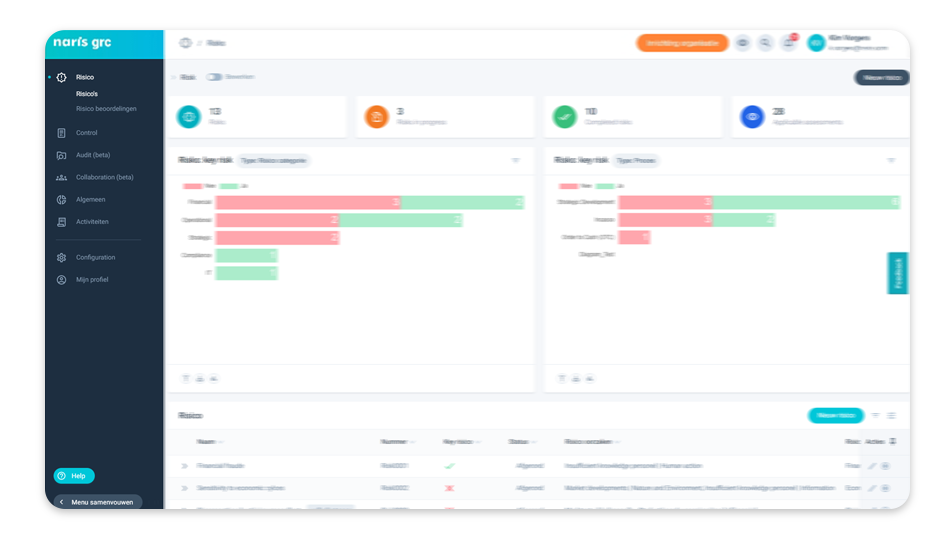
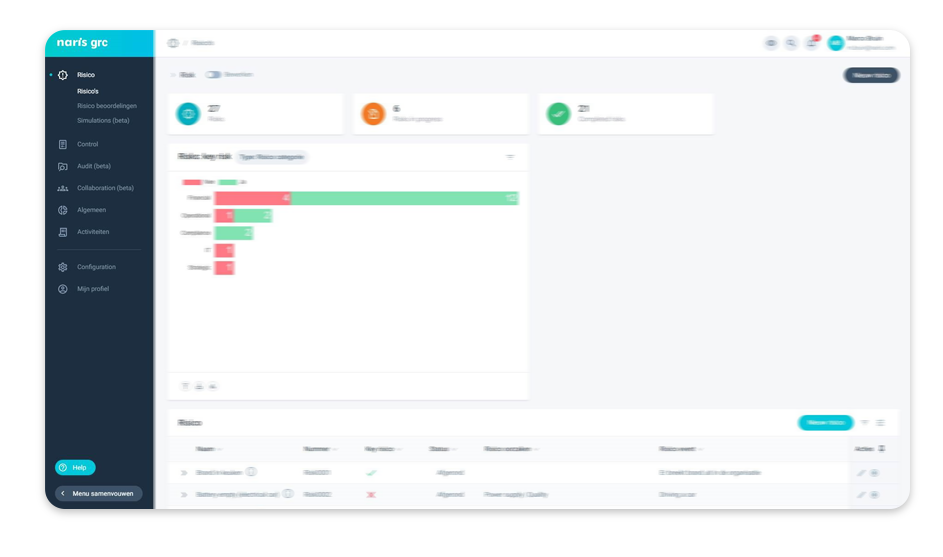
Gathering Input from Stakeholders
Stakeholders often have difficulty making a valuable contribution to successful GRC. Converting “their world of experience” into a standard language of risk analysis turns out to be very complex. GRC software enables stakeholders to easily list and prioritize risks. It also helps to arrive at a joint analysis in which elements such as determining probability x impact are experienced as fun. It also contributes to the life cycle of risks and the monitoring of measures.
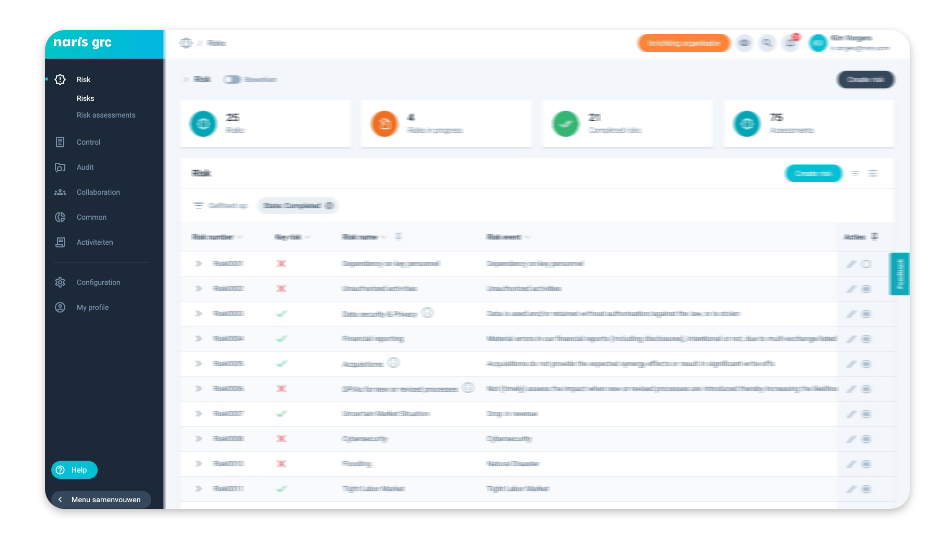
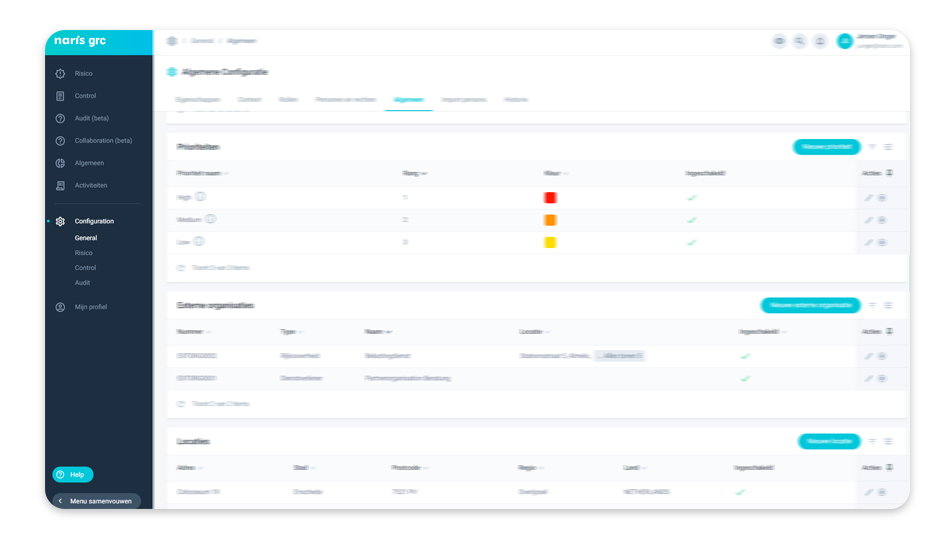
From Excel Chaos to Overview and Priority
Organizations often start by performing risk analyses in Excel. An excellent step towards a structured approach to risk management! However, this quickly leads to Excel-chaos, and a higher maturity level demands more. GRC software enables growth from risk analysis to risk management through overview, prioritization and control, in form of heatmaps, reports and links with measures and actions – an all-in-one GRC platform.
Monte Carlo simulation
Not all risks occur in full at the same time. With the Monte-Carlo simulation, 10,000 draws are made and statistically calculated what a necessary risk reserve should be. In NARIS GRC it is possible to independently perform Monte-Carlo simulations at multiple levels
Risk dialogue
As a risk manager, you should especially enter into a discussion about the risks with the organization. With Naris GRC it is possible to vote on risks before and after control measures. This can even be done anonymously to prevent voice influencing. After discussing the differences in perception, you as a facilitator can give a final value to the opportunity and impact.
The 8 steps of risk analysis
Handy infographic about the 8 most important steps

Inspiration around risk analysis.

GRC – Is it a Necessity?
Topics for Discussion As a Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) expert, there are a number of discussion topics that are

Don’t Become a Lone Wolf!
One of the most interesting statements I recently heard from the CEO of a large company was about the usefulness

NARIS launches groundbreaking integral GRC software
Today, NARIS GRC announces the launch of their fully updated – and expanded – Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) software.
Want to know more about risk analysis?
Do you have questions about the way in which you can perform smart risk analyses? Contact us without obligation!
Fill out the form or
call Floor:

Call me back!
Would you like to know what we can do for your organization? Fill in the form below.



